Estimate distillable entanglement and quantum capacity by squeezing useless entanglement
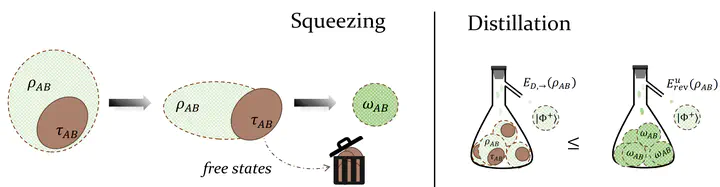 Illustration of the main result.
Illustration of the main result.Abstract
Quantum Internet relies on quantum entanglement as a fundamental resource for secure and efficient quantum communication, reshaping data transmission. In this context, entanglement distillation emerges as a crucial process that plays a pivotal role in realizing the full potential of the quantum internet. Nevertheless, it remains challenging to accurately estimate the distillable entanglement and its closely related essential quantity, the quantum capacity. In this work, we consider a general resource measure known as the reverse divergence of resources which quantifies the minimum divergence between a target state and the set of free states. Leveraging this measure, we propose efficiently computable upper bounds for both quantities based on the idea that the useless entanglement within a state or a quantum channel does not contribute to the distillable entanglement or the quantum capacity, respectively. Our bounds can be computed via semidefinite programming and have practical applications for purifying maximally entangled states under practical noises, such as depolarizing and amplitude damping noises, leading to improvements in estimating the one-way distillable entanglement. Furthermore, we provide valuable benchmarks for evaluating the quantum capacities of qubit quantum channels, including the Pauli channels and the random mixed unitary channels, which are of great interest for the development of a quantum internet.